Econometrics I
TA Christian Alemán
Session 2: Tuesday 1st, February 2022
Activity 1: Basic Matrix Operations
A simple structural national income model
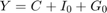
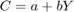
Boring solution:
![$Y^{*} = \frac{1}{1-b}[I_{0}+G_{0}+a]$](s2_eq00238636735775643446.png)
![$C^{*} = \frac{1}{1-b}[b(I_{0}+G_{0})+a]$](s2_eq10205195815201881564.png)
Using Linear Algebra: Transform to 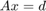 form
form
![$A = \left[\begin{array}{cc}1 & 0 \\ 0 & a \end{array}\right]$](s2_eq07288002101229768351.png) ,
, ![$x = \left[\begin{array}{c}Y \\ C \end{array}\right]$](s2_eq10061357105286525760.png) ,
, ![$d = \left[\begin{array}{c}I_{0}+G_{0} \\ a \end{array}\right]$](s2_eq13145882043246743807.png)
% Housekeeping clear all close all clc % par.b = 0.5; % Propensity to consume par.a = 1; % Basic Consumption par.I = 0; % Investment par.G = 0.2; % Goverment Spending A_mat = [1,-1;-par.b,1]; d_vec = [par.I+par.G; par.a]; % Boring Solution: Y_an = 1/(1-par.b).*(par.I+par.G+par.a); C_an = 1/(1-par.b).*(par.b*(par.I+par.G)+par.a); disp([]) opt.v_names = {'Y','C'}; c_table = array2table([Y_an,C_an],'VariableNames',opt.v_names); disp('Boring Solution') disp('') disp(c_table) % Using Linear Algebra: x = inv(A_mat)*d_vec; x = A_mat\d_vec; c_table = array2table(x','VariableNames',opt.v_names); disp('Solution with linear algebra') disp('') disp(c_table)
Boring Solution
Y C
___ ___
2.4 2.2
Solution with linear algebra
Y C
___ ___
2.4 2.2
Activity 2: Inverses and their properties
Define the inverse of matrix 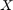 as
as 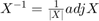
Such that 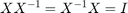
-The inverse is a derived matrix that may not exist.
-The inverse of a matrix is defined if:
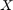 is a square matrix and
is a square matrix and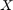 is is said to be nonsingular. Non-singularity:
is is said to be nonsingular. Non-singularity:  squareness and linear independence
squareness and linear independence
- More in Non-Singularity:
- A singular matrix has determinant equal to zero
- A nonsingular matrix hasa non-zero determinant.
2.1 Linear independence
Let 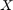 be matrix
be matrix 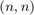
and  a column vector
a column vector 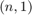 collecting the
collecting the  row vectors in
row vectors in 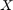
Linear independence requiers that the only set of scalars 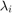 which can satisfy:
which can satisfy:
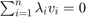
are 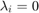 for all
for all 
Example 1:
![$X = \left[\begin{array}{ccc}3 & 4& 5 \\ 0 & 1&2 \\ 6&8&10\end{array}\right] = \left[\begin{array}{c}v_{1}\\v_{2}\\v_{3}\end{array}\right]$](s2_eq02143686478653965004.png)
the rows are not linearly independent because 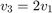
(i.e) ![$\lambda = [2;0;-1]$](s2_eq01173836379530996867.png)
% A Singular Matrix:
X_mat = [3,4,5;0,1,2;6,8,10];
X_mat(3,:)-2.*X_mat(1,:)
ans =
0 0 0
A non-singular matrix:
Y_mat = magic(3);
2.2 Eigenvalues and Determinants
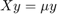
Let the 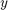 value that solves the above system of equations be called an eigenvector
value that solves the above system of equations be called an eigenvector
and 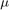 be the respective eigen value
be the respective eigen value
Define the trace of a Matrix as:
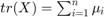
Define the determinant of a Matrix as:
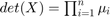
Example 2:
% Using Matlab In-built disp('Using Matlab In-Built') disp([det(X_mat),det(Y_mat)]) % Using our function disp('Using Our Function') disp([my_det(X_mat),my_det(Y_mat)])
Using Matlab In-Built
0 -360
Using Our Function
0 -360.0000
2.3 The rank of a matrix
The (row) rank of a matrix is defined to be the maximum number of linearly independent rows.
i.e the rank of a matrix is the number of non-zero row in the row-echelon form of the matrix.
Redefining Conditions for the existence of an inverse
The inverse of a squaren matrix exists if and only if it is of full rank.
Example 3:
% Use matlab in-built function disp('Using Matlab In-Built') disp([rank(X_mat),rank(Y_mat)]) % Use our function disp('Using Our Function') disp([my_rank(X_mat),my_rank(Y_mat)])
Using Matlab In-Built
2 3
Using Our Function
2 3
2.4 The inverse of a Matrix (if it exists)
Use matlab in-built function
disp(inv(Y_mat)) disp(my_inv(Y_mat))
0.1472 -0.1444 0.0639 -0.0611 0.0222 0.1056 -0.0194 0.1889 -0.1028
Use our function
disp(my_inv(Y_mat))
0.1472 -0.1444 0.0639 -0.0611 0.0222 0.1056 -0.0194 0.1889 -0.1028
2.5 Symetric and Idempotent Matrices
2.5.1 Symetry
A square matrix 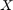 that satisfies the property
that satisfies the property 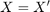 is said to be symmetric.
is said to be symmetric.
2.5.2 Idempotent
A square matrix 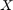 is idempotent if
is idempotent if 
If the matrix is symetric it follows that 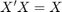
Idempotent matrices have that 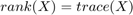
Idempotent matrices are very important in econometrics: Let 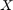 be an (n,k) matrix of data of
be an (n,k) matrix of data of 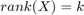 . Then the matrix
. Then the matrix 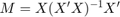
Example 4:
The data generating process
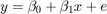 Where
Where 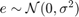
% Number of observation rng(4567) par.n = 500; % Simulate x par.mean_x = 4; par.variance_x = 2; par.variance_e = 0.1; x = par.mean_x +sqrt(par.variance_x).*randn(par.n,1); % Simulate error e = 0 + sqrt(par.variance_e).*randn(par.n,1); % Simulate Data Generating Process: par.beta0 = 2; par.beta1 = 0.5; y = par.beta0 + par.beta1.*x +e; % Show that $M=X(X'X)^{-1}X'$ is idempotent M = x*inv(x'*x)*x'; M_new = M*M; I = (M-M_new).^2; disp('Total Squared Diference:') disp(sum(I,'all'))
Total Squared Diference: 6.8891e-32
Activity 3: Least Squares Estimation:
Estimate the above model using Least Squares
Example 5:
Least Squares Estimate our function
vars = ols_esti(y,[ones(par.n,1) x]);
opt.v_names = {'\beta_{0}','\beta_{1}'};
c_table = array2table(vars.beta_hat','VariableNames',opt.v_names);
disp('OLS estimates: Our Function')
disp(c_table)
% Least Squares Estimate In-Built function
vars.beta_matlab = regress(y,[ones(par.n,1) x]);
c_table = array2table(vars.beta_matlab','VariableNames',opt.v_names);
disp('OLS estimates: In-built')
disp(c_table)
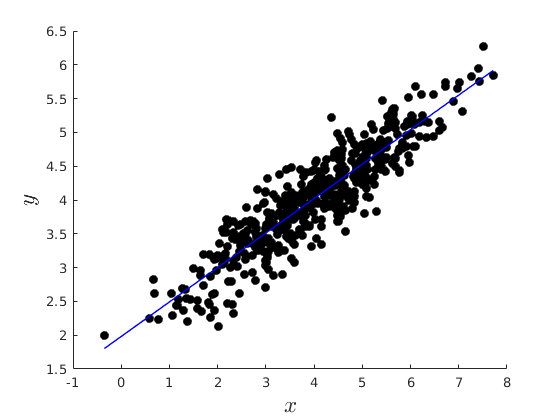
% figure
figure(1)
hold on
plot(x,y,'ko','MarkerFaceColor','k')
plot(x,vars.y_hat,'b-','linewidth',1.1)
xlabel('$x$','fontsize',17,'interpreter','latex')
ylabel('$y$','fontsize',17,'interpreter','latex')
here
OLS estimates: Our Function
\beta_{0} \beta_{1}
_________ _________
1.9818 0.51008
OLS estimates: In-built
\beta_{0} \beta_{1}
_________ _________
1.9818 0.51008
Activity 4: Using the Symbolic toolbox to do stuff
In this case to find the inverse of a matrix
My take(purely personal): AVOID using symbolic stuff, not helpfull at all.
syms a11 a12 a13 b21 b22 b23 c31 c32 c33 A_m = [a11,a12,a13;b21,b22,b23;c31,c32,c33]; A_inv = inv(A_m); disp(A_inv) syms a A_m = [sym(1),sym(0),sym(0);sym(0),sym(1),sym(0);sym(0),sym(0),a]; A_inv = inv(A_m); disp(A_inv)
[ (b22*c33 - b23*c32)/(a11*b22*c33 - a11*b23*c32 - a12*b21*c33 + a12*b23*c31 + a13*b21*c32 - a13*b22*c31), -(a12*c33 - a13*c32)/(a11*b22*c33 - a11*b23*c32 - a12*b21*c33 + a12*b23*c31 + a13*b21*c32 - a13*b22*c31), (a12*b23 - a13*b22)/(a11*b22*c33 - a11*b23*c32 - a12*b21*c33 + a12*b23*c31 + a13*b21*c32 - a13*b22*c31)] [-(b21*c33 - b23*c31)/(a11*b22*c33 - a11*b23*c32 - a12*b21*c33 + a12*b23*c31 + a13*b21*c32 - a13*b22*c31), (a11*c33 - a13*c31)/(a11*b22*c33 - a11*b23*c32 - a12*b21*c33 + a12*b23*c31 + a13*b21*c32 - a13*b22*c31), -(a11*b23 - a13*b21)/(a11*b22*c33 - a11*b23*c32 - a12*b21*c33 + a12*b23*c31 + a13*b21*c32 - a13*b22*c31)] [ (b21*c32 - b22*c31)/(a11*b22*c33 - a11*b23*c32 - a12*b21*c33 + a12*b23*c31 + a13*b21*c32 - a13*b22*c31), -(a11*c32 - a12*c31)/(a11*b22*c33 - a11*b23*c32 - a12*b21*c33 + a12*b23*c31 + a13*b21*c32 - a13*b22*c31), (a11*b22 - a12*b21)/(a11*b22*c33 - a11*b23*c32 - a12*b21*c33 + a12*b23*c31 + a13*b21*c32 - a13*b22*c31)] [1, 0, 0] [0, 1, 0] [0, 0, 1/a]
%------------------------------------------------------------------------- % Adjoint Function function AD = my_adjoint(X) %{ This function computes the adjoint matrix of a square matrix Input: X: Square matrix Output: D: adjoint of the matrix X %} [N,M] = size(X); if N~=M error('Input matrix not a square matrix.') end C = NaN(N,N); for ki=1:N for kj = 1:N % Compute the cofactor matrix C(ki,kj) = (-1)^(ki+kj)*det(X([1:ki-1 ki+1:N],[1:kj-1 kj+1:N])); end end AD = C'; end %------------------------------------------------------------------------- % Inverse function function [inv_mat] = my_inv(X) %{ This function computes the Inverse of a square matrix if it exists Input: X: Square matrix Output: inv_mat: Inverse of the matrix X %} [N,M] = size(X); if N~=M error('Input matrix not a square matrix.') end if rank(X)~=N error('Input matrix not full rank.') end inv_mat = (1/det(X)).*my_adjoint(X); end %------------------------------------------------------------------------- % Determinant function function [D] = my_det(X) %{ This function computes the Determinant of a square matrix Input: X: Square matrix Output: D: determinant of the matrix X %} [N,M] = size(X); if N~=M error('Input matrix not a square matrix.') end eig_val = eig(X); % Eigen values D = prod(eig_val); if abs(D)<1e-13 D = 0; end end %------------------------------------------------------------------------- % Rank function function [rank] = my_rank(X) %{ This function computes the rank of a square matrix Input: X: Square matrix Output: rank: rank of the matrix X %} [N,M] = size(X); if N~=M error('Input matrix not a square matrix.') end ech_mat = rref(X); % Echelon reduction sum_ech_mat = sum(abs(ech_mat),2); I = sum_ech_mat==0; rank = N - sum(I); end %------------------------------------------------------------------------- % OLS function [vars] = ols_esti(y,X) %{ This function computes the Least Squares Estimate Input: y: Dependent Variable (N,1) X: Independent Variables (N,K) Output: Many stuff you saw in class. %} [par.Nx,par.K] = size(X); % N=no.obs; K=no.regressors [par.Ny] = size(y,1); % if par.Ny~=par.Nx error('X and y do not have same length') end par.N = par.Nx; % Save number of regressots vars.beta_hat = X\y; % Coefficients: vars.beta_hat_alt = inv(X'*X)*(X'*y); % Predicted values: vars.y_hat = X*vars.beta_hat; % Residuals: vars.e_hat = y-X*vars.beta_hat; % Total Variation of the dependent variable vars.SST = (y - mean(y))'*(y - mean(y)); % (SSE) Sum Squared Residuals vars.SSE = vars.e_hat'*vars.e_hat; % SSR/SST or "r-squared" is the ratio of the variation in y explained by the model and the total variation of y vars.R2 = 1 - (vars.SSE/vars.SST); % Adjusted "r-squared". vars.R2A = 1 - (vars.SSE/(par.N-par.K))/(vars.SST/(par.N-1)); vars.sigma2_hat = vars.SSE/(par.N-par.K); %Variance of estimator: vars.var_covar = vars.sigma2_hat*inv(X'*X); vars.SEbeta_hat = sqrt(diag(vars.var_covar)); disp('here') end
0.1472 -0.1444 0.0639 -0.0611 0.0222 0.1056 -0.0194 0.1889 -0.1028